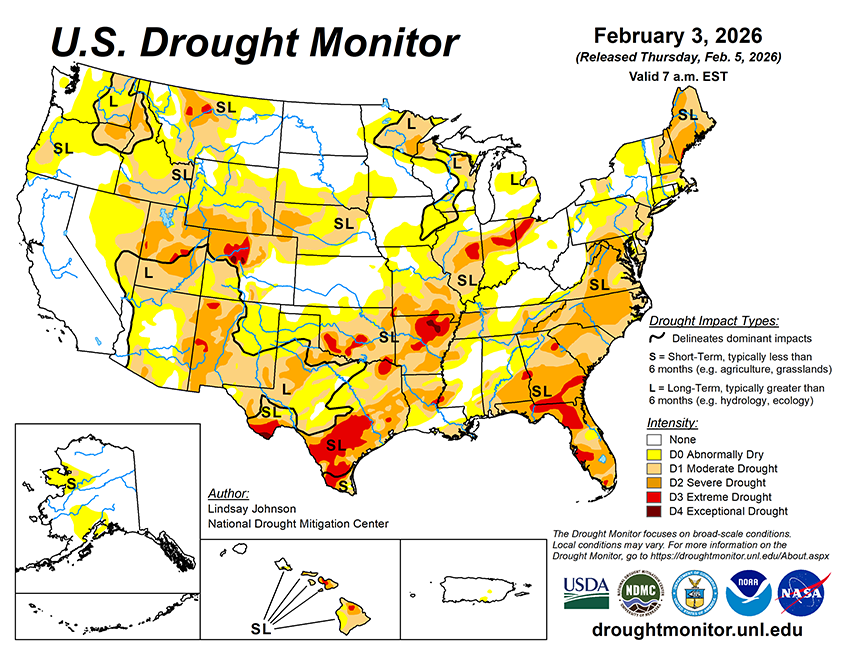
Over the next five to seven days, an active weather pattern is expected across much of the continental U.S., with several regions showing a strong signal for precipitation. The heaviest precipitation is forecast from the lower Mississippi Valley northeastward into the Ohio and Tennessee valleys, where widespread totals of 1 to 3 inches are expected, with locally higher amounts possible. Portions of the central Plains, Midwest, and Great Lakes are anticipated to receive generally 0.5 to 1.5 inches of precipitation during this period. Across the West, precipitation is expected to be widespread from the Pacific Northwest into the northern and central Rockies. Liquid-equivalent totals of 1 to 3 inches are forecast in the Cascades and northern Rockies, with locally higher amounts possible at higher elevations. Farther south into the Great Basin and Southwest, precipitation becomes more scattered, with most areas receiving less than 0.5 inches, and many locations remaining dry. Drier conditions are expected to persist across California, the northern Great Plains, central and southern Texas, and much of the Florida Peninsula, where little to no precipitation is forecast over the next week.
The Climate Prediction Center’s 6–10 day temperature outlook (Feb. 10-14) shows a strong and widespread signal for above-normal temperatures across much of the continental U.S. The highest probabilities of above-normal temperatures are centered over the central and southern Plains, extending northward into the northern Plains and Upper Midwest. Much of the Intermountain West, Rockies, and interior West also favors above-normal temperatures. Along the West Coast, temperatures are expected to be near normal, while parts of the Northeast show a transition from below normal in northern New England to near or above normal farther south. Portions of the Southeast, including Florida, are favored to see near-normal temperatures. Alaska shows a mix of near- to below-normal temperatures across the mainland, with near-normal conditions favored over the southern coast. Hawaii is favored to experience above-normal temperatures during this period.
The Climate Prediction Center’s 6–10 day precipitation outlook (Feb. 10–14) favors above-normal precipitation across much of the western U.S., including the Southwest and West Coast, with elevated probabilities extending into parts of the northern Rockies. Above-normal precipitation is also favored across Alaska and Hawaii during this period. In contrast, below-normal precipitation is favored across Florida and portions of the far Southeast, while much of the central U.S. is expected to see near-normal precipitation.